Shariq Mohammed
Assistant Professor of Biostatistics
Boston University
Biography
I am an Assistant Professor in the Department of Biostatistics at Boston University School of Public Health and a Rafik B. Hariri Junior Faculty Fellow (2022-2025) at BU’s Hariri Institute for Computing and Computational Science & Engineering. I build statistical models and computational tools that turn high‑dimensional, complex‑structured data into clinically useful insight.
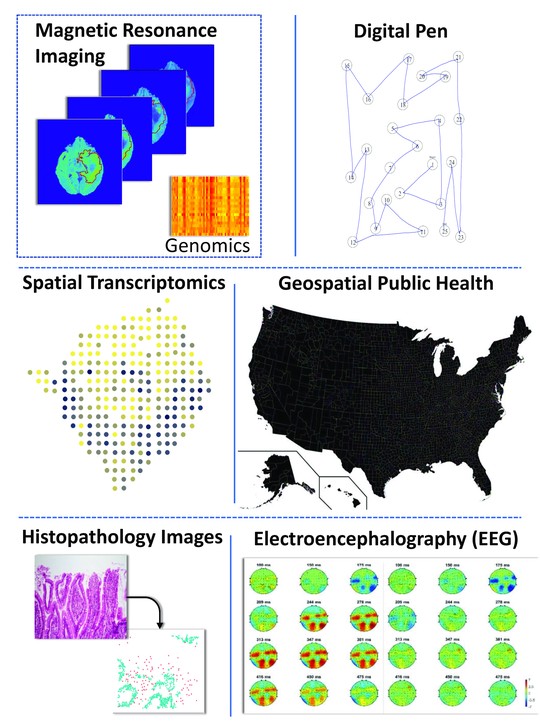
My group develops methods at the interface of hierarchical Bayesian modeling, variable selection, functional & geometric data analysis, spatial statistics, network models. We work with digital, spatial‑omic, geospatial, and imaging data, with applications in neurodegenerative disease (with a focus on dementia and Alzheimer’s disease) and oncology. Our research aims to develop interpretable features, reliable prediction models, and biological explanations that support better decisions in patient and public health.
Before BU, I was a postdoctoral research fellow in Biostatistics and in Computational Medicine & Bioinformatics at the University of Michigan–Ann Arbor, and a Precision Health Scholar. I received my Ph.D. in Statistics from the University of Connecticut.
Interests
- Bayesian Modeling
- Variable Selection
- Functional / Geometric Data Analysis
- Spatial Statistics
- Medical Imaging Analysis
- Digital & Spatial‑Omic Data
- Geospatial Methods
- Neurodegeneration & Cancer
Education
-
Ph.D. in Statistics, 2018
University of Connecticut
-
M.S. in Statistics, 2017
University of Connecticut
-
M.Sc. in Applications of Mathematics, 2014
Chennai Mathematical Institute
-
B.Math.(Hons.), 2012
Indian Statistical Institute